Tobacco, cotton and sugar were grown on large-scale farms called plantations.
As European demand for these crops increased, the plantations grew larger and needed more slaves to harvest the crops.
80% of all slaves shipped to the Americas were put to work on plantations. They worked long hours in the fields and were punished if they did not work hard enough.
Other slaves worked in the house as servants, or were used to do other jobs around the plantation.
The picture below is an artist’s impression of a plantation.
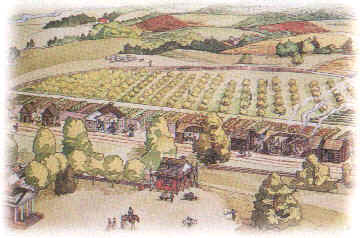
Drawing by G. B. McIntosh Thomas Jefferson Foundation Inc.
Plantation Owner’s House
The owners of plantations were very rich and lived in big houses with many rooms. The area around the house would often be planted with plants and flowers.
Slave Huts
The slaves were housed in sparsely furnished wooden huts. Their huts were grouped together, often fairly close to the plantation fields.
Livestock
Many plantations kept cows, sheep and chickens to provide them with fresh meat, milk and eggs.
Plantation Fields
Most plantations tended to concentrate on growing just one product – tobacco, cotton or sugar were the most common. They were grown on a large scale in one or more fields. Slaves were responsible for the ploughing, sowing and harvesting of the crop and were punished if they did not work hard enough.
House Slaves
The house slaves – cooks, maids, nannies, butlers and drivers, were often housed separately to the field slaves. Their living quarters were generally better than those who worked in the fields and were placed fairly close to the plantation owner’s house.
Blacksmith
Slaves were taught the blacksmith’s craft. Their jobs included mending broken ploughs, making and repairing farm and garden tools as well as shoeing horses.
Vegetable Garden
Slaves who were not fit enough for the heavy work in the fields would be put to work in the plantation gardens. Vegetables grown in the garden would include peas, beans, carrots and pumpkins.
Woodworking Hut
Many plantations had their own woodworking huts. This was where furniture and floorboards were made by white craftsmen often assisted by black slaves.
Fruit Garden
Many plantations had their own orchards growing apple, pear, peach, plum and cherry trees. Some plantations even had their own vineyards and produced their own wine.
Weaver’s House
The plantation weaver would be responsible for making all the furnishings such as curtains and coverings for the house.
Overseer’s House
Plantation owners usually employed a white overseer or manager to look after the day to day running of the plantation. These men would also be responsible for making sure that the slaves were working as hard as they could and would carry out punishments if they thought the slaves were slacking.
Storehouse
The storehouse was used to store crops awaiting sale. It was also used to store new tools, furniture or furnishings.
This article is part of our extensive resources on black history. For a comprehensive article on black history in the United States, click here.
Cite This Article
"Black Peoples of America – The Plantation" History on the Net© 2000-2024, Salem Media.
April 20, 2024 <https://www.historyonthenet.com/black-peoples-of-america-the-plantation>
More Citation Information.







