For more information on Native American tribes and other counter-intuitive facts of ancient and medieval history, see Anthony Esolen’s The Politically Incorrect Guide to Western Civilization.
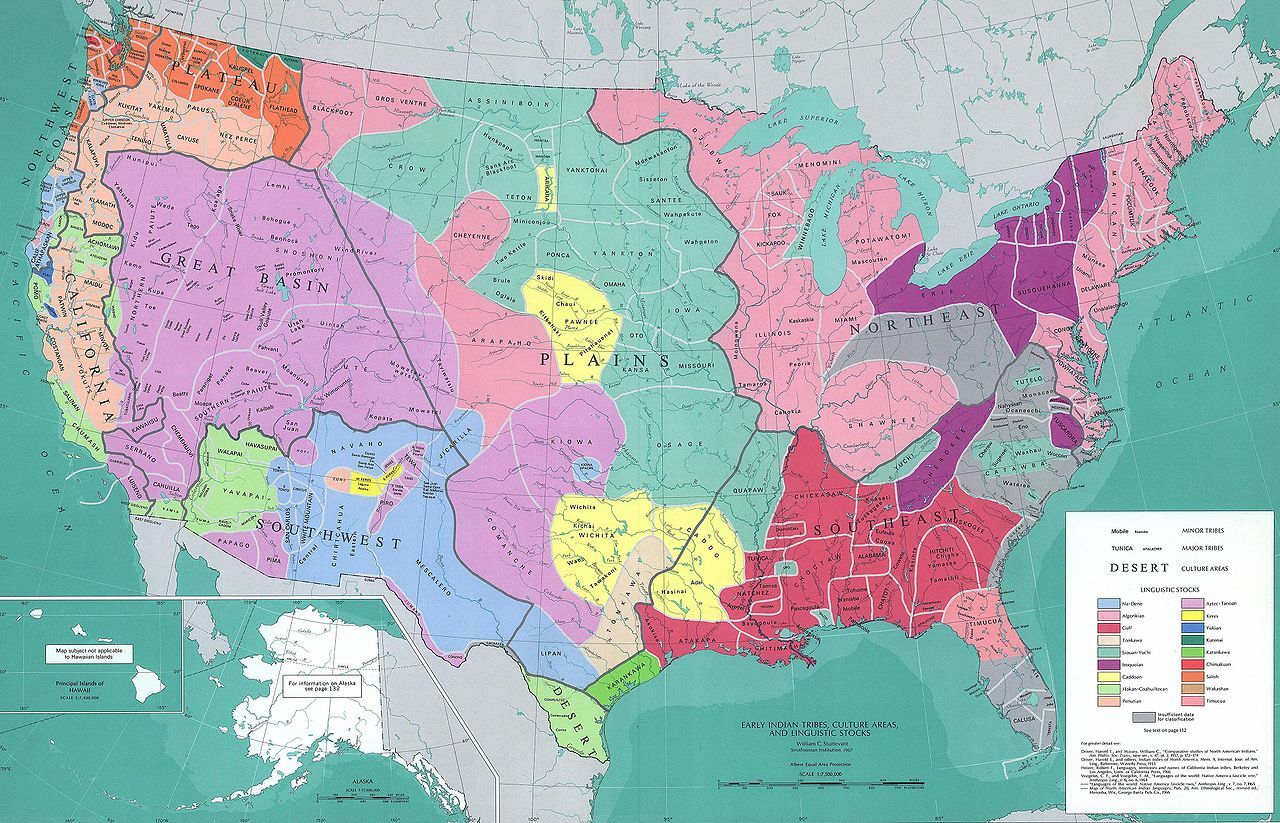
There were many different Native American tribes and those with similar characteristics formed a main tribe or nation. Each had its own language, religion and customs.
For the most part the Native American tribes lived peaceably believing that nature was sacred and was to be shared. However, the coming of the Europeans and the removal of their land led to conflict both between the different Native American tribes and between the Indians and whites.
By the end of the nineteenth century the Native American tribes had lost their fight to preserve their traditional way of life and those that had survived the conflicts were confined to reservations. This was the way of life for Native American tribes.
“The Pilgrims and Native Americans Were Both On the Verge of Death Upon Meeting. Here’s How They Saved Each Others’ Lives.”
For the full “History Unplugged” podcast, click here!
The table below gives a summary of each of the main Native American tribes of the Plains.
Native American Tribes’ Names | Nomadic/ Static | Native American Tribes’ Famous Leaders | Native American Tribes’Brief Facts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apache | Nomadic Hunter-gatherer | Geronimo, Cochise | Made up of several different groups Lived in extended family units Usual shelter was a dome-shaped lodge called a wickiup Polygamy was allowed but rarely practised Reliant on the buffalo Frequent disputes with the Comanches led to their weakening in the 1700s Traded with the Pueblas in Mexico or raided Spanish villages for goods and horses 1861 conflict between Apaches led by Cochise and Americans in protest at being forced onto reservations 1874 a group of Apaches led by Geronimo escaped capture and fled to Mexico 1886 Geronimo forced to surrender and taken to Fort Marion in Florida |
| Arapaho | Nomadic Hunters | Usual shelter was a tipi Women were in charge of the home and owned the tipi Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Reliant on the buffalo Perform Sun Dance in the summer Frequent conflicts with Shoshone and Pawnee Native American tribes 1864 Arapaho were among those slaughtered in the Sand Creek Massacre 1867 placed on Oklahoma reservation 1876 Northern Arapaho placed on Wind River reservation in Wyoming 1889 Active in bringing about the Ghost Dance movement | |
| Blackfoot | Nomadic Hunter-gatherer | Crowfoot | Made up of several different groups Usual shelter was a tipi Women were in charge of the home and owned the tipi In this Native American tribe, Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Polygamy was usual Reliant on the buffalo Performed Sun Dance in the summer Mid 1800s many killed by smallpox 1870 200 killed in the Marias Massacre |
| Cherokee | Static Hunter-farmer | Sequoyah | Made up of seven different clans Usual shelter was cane and mud plaster huts Women were in charge of the home and land Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Grew corn, beans, squash, and sunflowers Used canoes 1821 Sequoyah invented the Cherokee alphabet 1838-9 moved west to Oklahoma (Trail of Tears – 4000+ died on the 800 mile journey) |
| Cheyenne | Nomadic Hunter-gatherer | Black Kettle | Made up of ten different bands Allied with Arapaho and Sioux Usual shelter was a tipi Women were in charge of the home and owned the tipi Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Reliant on the buffalo 1864 Cheyenne were among those slaughtered in the Sand Creek Massacre 1876 Northern Cheyenne took part in the Battle of the Little Bighorn 1877 Many forced to Oklahoma those that resisted were shot |
| Comanche | Nomadic Hunter-gatherer | Established around 1700 after breaking away from Shoshone Led by Peace Chief and War Chief Usual shelter was a tipi Women were in charge of the home and owned the tipi Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Reliant on the buffalo Frequent conflicts with Apache and Spanish 50% killed by smallpox and cholera in the mid 1800s 1874-5 Took part in the Buffalo War (Red River War) in protest at the numbers of buffalo being slaughtered By 1879 most were on Fort Sill reservation | |
| Crow | Nomadic Hunter-gatherer | Medicine Crow | Established around 1700 after breaking away from the Sioux Two Native American tribes – Mountain Crow and River Crow Usual shelter was a tipi Women were in charge of the home and owned the tipi Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Reliant on the buffalo Frequent conflict with Sioux, Shoshone and Blackfoot 1851 Given 35 million acres of land 1868 Land reduced to 8 million acres 1870 Placed on reservation in Oklahoma |
| Navajo | Semi-Nomadic Hunter-farmer | Moved to south-west around 1500 Usual shelter was a hogan (round stick house covered with mud or hides) Women were in charge of the home and owned the hogan Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Kept sheep and women spun and wove wool into cloth Traded with the Spanish Frequent conflict with Spanish Conflict with Americans following Mexican War 1849 1863 American force under Kit Carson killed Navajo sheep 1863-4 Forced to move 300 miles to Fort Sumner (The Long Walk) many died on the way 1869 Placed on reservation and given 30,000 sheep by US governement | |
| Nez Perce | Semi-Nomadic Hunter gatherer | Chief Joseph | Made up of two groups – Upper and Lower Nez Perce Name given by the French on account of the tribe piercing their noses Usual shelter originally a longhouse but later used tipis Women were in charge of the home Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Made canoes and fished for salmon Frequent conflict with Crow and Shoshone 1863 Allocated land reduced by 7 million acres 1877 Under Chief Joseph actively resisted being moved to reservation (Nez Perce War) Defeated at the Battle of Bear Paw Mountains |
| Pawnee | Semi-Nomadic Hunter-farmer | Made up of four different bands Usual shelter was an earth lodge but used tipis when hunting Women were in charge of the home Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Many killed by smallpox and cholera in the mid 1800s 1825 recognised supremacy of US government 1830-1860 – gave up increasing amounts of land to US government Many Pawnee became scouts for the US government 1876 Moved to Oklahoma reservation | |
| Shawnee | Nomadic Hunter-farmer | Tecumseh, Black Hoof | This Native American Tribe was made up of five different groups Allied with Cherokee Usual shelter was a wikkum or wigwam (small round dwelling) Women were in charge of the home and farming corn Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Used canoes 1740-1760 Caught up in the conflict between the French and British over Ohio Some fought for the British in the War of Independence while others remained neutral Tecumseh led resistance against American expansion but was killed in 1813 Black Hoof led resistance against Indian removal until his death in 1831 1832 Shawnee tribe were living on reservations |
| Shoshone | Nomadic Hunter-gatherer | Pocatello, Bear Hunter | Made up of seven different groups Usual shelter was a tipi but some lived in brushwood shelters Women were in charge of the home and owned the tipi Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Reliant on the buffalo Driven from their land by Mormon settlement of Utah 1862 Bear Hunter led a series of raids on Mormon livestock 1863 Bear Hunter and 250 Shoshone killed in Bear River Massacre After 1863 remaining Shoshone moved to Fort Hall reservation |
| Sioux | Nomadic Hunter | Red Cloud, Sitting Bull | Made up of seven different groups Largest Native American tribe Usual shelter was a tipi Women were in charge of the home and owned the tipi Men were in charge of hunting for food and protecting the camp Reliant on the buffalo Performed the Sun Dance in the summer 1862 Group led by Little Crow massacred 800 settlers in Minnesota 1866-68 Red Cloud led resistance to white settlement along the Bozeman Trail (Red Cloud’s War) 1876 The Native American tribe took part in the Battle of the Little Bighorn 1890 Finally defeated at Battle of Wounded Knee |
For more on the Native American tribes, see below:
For more information on Native American tribes and other counter-intuitive facts of ancient and medieval history, see Anthony Esolen’s The Politically Incorrect Guide to Western Civilization © 2008. You can find it at Amazon or Barnes & Noble.
You can also check it out by clicking on the buttons to the left.
This article is part of our larger resource on the American West culture, society, economics, and warfare. Click here for our comprehensive article on the American West.
Additional Resources About American West and Native Americans
Cite This Article
"Native American Tribes and Nations: A History" History on the Net© 2000-2024, Salem Media.
April 24, 2024 <https://www.historyonthenet.com/native-american-tribes-nations>
More Citation Information.